It is almost impossible for someone to truly learn something without also having the memory to retain what they learned.


At the beginning of my parenting journey, I came across this quote, “There are only two lasting bequests we can hope to give our children. One of these…is roots, the other, wings.”

According to Quote Investigator, the earliest evidence of this saying comes from a book by a prominent 1953 newspaper editor, Hodding Carter, in which he said a “wise woman” said those words to him.
One day, I would like to meet Ms. Anonymous. Many profound statements have been made by her.
When I first learned that my daughter was dyslexic, I was crushed. The plans I had; the dreams I’d cherished disappeared the moment I read the dyslexia specialist’s evaluation report.
As in any other loss, I went through the grieving process.
Denial
First, I thought she had made a mistake. Perhaps my daughter had just misunderstood some of her questions and directions. My brilliant child could not have the D word.
Anger
“Why me?” I asked God. After all, I am the academic in my family. “Why would you do this to embarrass me?” My friends expected my daughter to be a genius. Now, instead I would be humiliated. I didn’t even know anyone with a dyslexic child.
Bargaining
If only I had spent more time teaching her the basics… If only I had homeschooled her… If only… If only… If only…
“Okay, God, I’ll do better. Can you make this go away?”
Depression
“I’m an introvert, so I’ll just keep to myself and tell no one,” I thought.
Acceptance
Finally, I arrived at a place of acceptance. This is the hand I was dealt, so God must have a good reason. After all, He said that all things work together for good to those who love Him. The time had come to buckle down, do some research, and tackle this monster. When all is said and done, I am more than a conqueror.
This was the point when I sat down, reflected, prayed, and made a plan. I am resilient – my mother taught me how. I am a winner – my father instilled that in me.
I picked up myself, dusted off my mental dross, and stepped out to vanquish dyslexia. I resolved to give my daughter roots and wings.
Roots so deep that no one could shake her belief in herself… her gifts and abilities.
Wings so wide that nothing would keep her from reaching her highest goal in life.
How to give your child roots and wings:
Most importantly, come to a place of acceptance quickly.
Make memories in elementary school:
Highlight her strengths and use them to build her weaknesses.
Counterbalance the negatives teachers and other authority figures pour into her.
Read about that in my first letter to her here.
Make memories during the middle school years:
Find and implement programs available to strengthen the weak skills. Not just the popular ones, but also try those that may only have anecdotal evidence. If they worked for someone else, they may work for you.
Travel. Let her see social studies in action in real life. Take her to various countries. Let her explore the real world.
Check out my letter recounting my daughter’s middle school experience.
Make memories while she is in high school:
Teach her self-advocacy. Help her discover how she learns and provide the support and encouragement for her to travel on her own. Let her build confidence in her ability to surmount the most challenging difficulties.
Discuss every topic she’s interested in. Be prepared for your knowledge and imagination to be stretched.
Give her space to grow into her personality. Look at her graduation letter here.
Be a safety net for her during her young adulthood:
When my daughter went away for college, I visited regularly, and we chatted on the phone frequently.
Her friends got acquainted with me and I became a mentor to some and a surrogate mom to others.
Throughout the years, at different intersections of life, my daughter thanked me for the way I raised her and the consistent support I gave.
She still has some challenges, but she has learned how to roll with them.
On the other hand, she has excelled in the areas of her gifting, and receives ongoing accolades.
Many years ago, I come across some books and tapes by Dr. Denis Waitley. This poem of his resonated with me, and I hope it does with you, too.
A poem to parents…from their teenage child If I had two wishes, I know what they would be I'd wish for Roots to cling to, and Wings to set me free; Roots of inner values, like rings within a tree, And Wings of independence to seek my destiny. Roots to hold forever to keep me safe and strong, To let me know you love me, when I've done something wrong; To show me by example, and help me learn to choose, To take those actions every day to win instead of lose. Just be there when I need you, to tell me it's all right, To face my fear of falling when I test my wings in flight; Don't make my life too easy, it's better if I try, And fail and get back up myself, so I can learn to fly. If I had two wishes, and two were all I had, And they could just be granted, by my Mom and Dad; I wouldn't ask for money or any store-bought things. The greatest gifts I'd ask for are simply Roots and Wings. By Denis Waitley
As you ponder the future, what is your major goal for your child?
The most common struggle dyslexics experience is an inability to read. They have extreme difficulty identifying letters, converting those letters into sounds and putting them together to make words.

During the times of the apprenticeship era, there was not the great need to read as there is today. People learned by observing and doing. Kinesthetic learning was the norm.
With the dawn of the industrial revolution, however, there arose the need to educate the masses to work in the resulting businesses.
The invention of the printing press merged perfectly with this need for mass education. This made it possible to put knowledge into a system that could be spread out on a national level. Hence, the proliferation of textbooks. Only then did those with dyslexic minds begin to have problems.

According to Dean Bragonier, founder and executive dyslexic of NoticeAbility, the dyslexic mind is able to “look at a situation, identify seemingly disparate pieces of information and blend those into a narrative or tapestry that makes sense” to them. Most people are unable to perceive the situation in the same way.
This ability translates into levels of exceptional success needed in some vocational paths, for example, entrepreneurship, engineering, architecture and the arts.
In spite of that, they are at a great disadvantage during their years in school.
There are three ways of accessing information: eye reading (print books), ear reading (recorded or audiobooks), and finger reading (braille). While information is commonly made available in braille for blind children, dyslexic children are mandated to eye read print books, and when they have trouble doing so, are labeled as lazy, stupid or unmotivated to learn.

Ear reading is not new. As early as 1931, the American Foundation for the Blind and the Library of Congress Book for the Blind Project established the Talking Book Program. Here is an abridged history of audiobooks:
1934: The first recordings are made for the Talking Book Program and include parts of The Bible, The Declaration of Independence, and Shakespeare’s plays.
1948: The Recording for the Blind program is founded (in 1995 renamed Recording for the Blind and Dyslexic, and in 2011 renamed Learning Ally).
1952: Caedmon Records is formed in New York and is a pioneer in the audiobook industry.
1955: Listening Library is founded and is the first to distribute audiobooks to libraries and schools.
1970s: Libraries start carrying audiobooks.
1985: Publishers Weekly identifies 21 audiobook publishers including Caedmon, Recorded Books, Books on Tape, Harper and Row, and Random House.
1980s: Bookstores start to display audiobooks on bookshelves instead of in separate displays.
1986: The Audio Publishers Association is created.
1997: Audible debuts the first digital audio player.
2011: Audiobook self-publishing becomes possible with the Audiobook Creation Exchange (ACX).
2012: Audiobook annual publication increases 125% from 7,200 to 16,309.
(Source: The Audio Publishers Association)
Dyslexic clinical psychologist, Dr Michael Ryan, gives some recommendations when using audiobooks:

With this longstanding history, I wonder why aren’t schools more accepting of ear reading as a method for testing the knowledge of those children who are dyslexic, and audiobooks for textbooks?
What has been your experience with audiobooks?
Have you used recorded textbooks for your children?
Today, I continue to put a megaphone to my voice to help children with dyslexia get the support they need to succeed – from parents, teachers, and everyone with whom they come into contact.

Most dyslexic people have strong visual/spatial abilities and weak auditory skills. How does that translate to real-life and living?
One important area that has significant consequence in childhood is following directions. This requires accessing of linguistic information presented in different forms.
Because this learning and thinking difference occurs on a spectrum, the level of difficulty following directions will vary from one dyslexic to another.
Some children have poor sight-word recognition but they are able to process language adequately. They understand phonics and apply it to reading, but have memory problems that translate to, among other things, following verbal or written directions.
Others have trouble processing language but are able to recognize sight words, so they rely on sight words when they see unknown words but are unable to sound them out. These children take mental pictures of word patterns and are able to read. These are the children who say “the” for any word that has that letter combination in it, like, their, there, them, they, etc.
Then there are those children with a mixture of the two. Their difficulty is a combination of the two experiences above.
In a very short video clip, Nessy illustrates how a child may appear to be lazy when, in fact, he has forgotten a direction given. Check it out here.
Instead of slapping labels on children who have difficulty following your directions, or punishing them for “deliberately” disregarding your instructions, seek ways of making the direction as easy as possible to visualize.
How have you felt when you could not remember all the instructions given to you or were distracted by something, then forgot directions you were following?
In 1967, Johnson and Myklebust stated that “a child who cannot read cannot write.” That makes sense, since some researchers, in their 2010 and 2011 studies, found that “reading and writing rely of related underlying processes.”

Just as they do with reading, most children with dyslexia have trouble with writing. This is demonstrated in a number of ways, for example, poor spelling, illegible penmanship, narrow vocabulary, weak idea development, and a lack of organization of thoughts.
You may hear a dyslexic child say, “I know what I want to say, but I just can’t write it down.”
Marianne Mullally, an Australian educator, explains it simply:
Just like their reading can be improved with time and various strategies, the writing of dyslexics can get better with explicit instructional strategies.
Keep in mind that reading must be worked on first. Michael Clark gives parents some tips and tricks to help their dyslexic children with their writing skills:
Now, here’s a fun activity. If you are non-dyslexic, do this exercise to experience what it is like for a dyslexic to take notes:
How did you do? Please share your thoughts with us.
Most people have one side of their body that’s stronger than the other. For example, if you’re right-handed, you probably do everything with your right hand – brush your teeth, comb your hair, write, eat, etc. That also means that, most likely, you have stronger sight in your right eye, stronger hearing in your right ear, and put your right foot into your trousers first. Why is that so?
As a child develops and interacts with her world, her brain slowly works through a configuration called lateralization, where one side of the brain takes charge, i.e. becomes the dominant side, while the other side becomes the supporting region.
Mostly, the left side of the brain takes control. That’s why most people are right-handed, because one side of the brain controls the opposite side of the body.
Are you wondering how to determine your child’s dominance?

It’s easy.
Those people who do not have that unilateral dominance are said to have mixed dominance, which is also known as cross dominance or crossed laterality. They prefer to do different activities with different sides of their body. For example, write with the right hand and eat with the left hand. This mixed dominance may cause the brain to be disorganized.
It has been said that people whose hand, eye, foot, or ear dominances are not consistently either right- or left-sided are at risk of experiencing academic difficulties.
This idea that there is a correlation between academic performance and mixed dominance has been gaining popularity, so in 2017, a group of researchers conducted a study to determine the impact of crossed laterality on academic achievement and intelligence. They did a systematic review and meta-analysis of the articles published on the topic, since 1900. They did not find strong evidence in favor of a relationship between crossed laterality and academic achievement.
Although these researchers found that mixed dominance does not cause learning disabilities, others have found that mixed dominance appears more often in children with dyslexia.
If your child is mixed dominant, there is no need to “fix” her dominance. Instead, focus on recognizing your child’s strengths, and engage her in brain lateralization exercises frequently, to ensure that her limbs cross the midline of her body.
Notwithstanding everything I’ve said here, remember that research has definitively shown that the brain can change.
If you don’t know your eye dominance, here is one way to find out:
Are you right or left eye dominant?
Only a few people have won an Emmy, a Grammy, an Oscar, and a Tony Award (EGOT). Caryn Elaine Johnson is one of them.
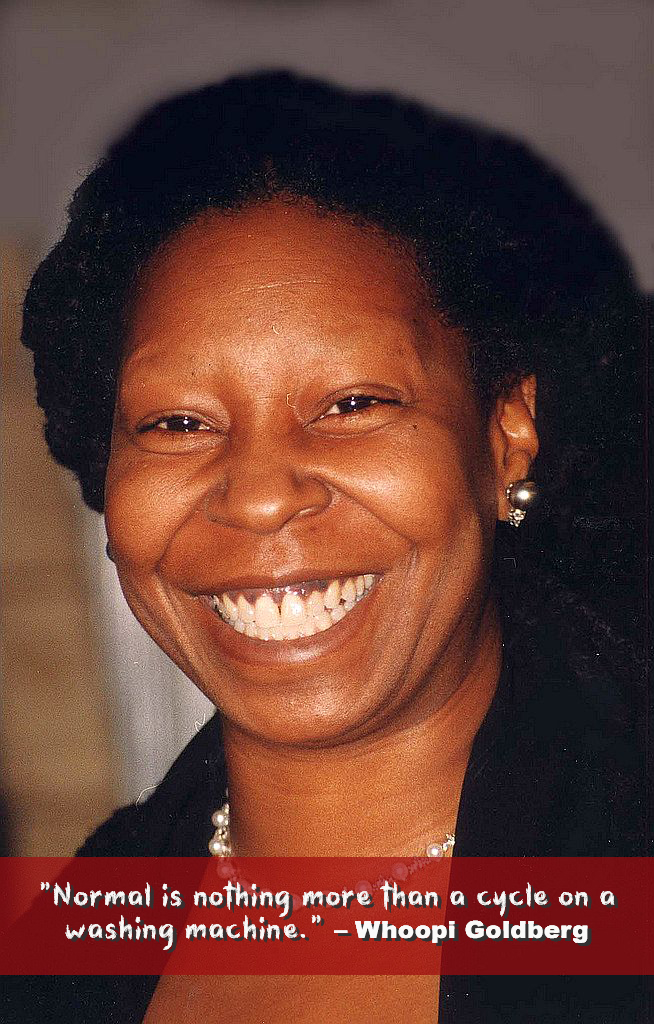

She was born on November 13, 1955 in Chelsea, New York and grew up in a housing project with her brother and mother, who was a nurse and later became a Head Start teacher.
In school, she was called “slow,” “dumb,” “lazy,” or “retarded.” She wasn’t diagnosed with dyslexia until she was an adult, so when school kept getting harder and harder, she eventually dropped out at 17. With her self-esteem low, she traveled a turbulent road in life, which included poverty, drug addiction, single motherhood, welfare, and a series of wide ranging jobs.
In his interview for the Child Mind Institute, the founder, Dr. Harold Koplewicz, called her a woman of grit and resilience.
Today, we know her as Whoopi Goldberg, actress, comedian, radio host, television personality, author and UNICEF International Goodwill Ambassador. Listen to her recall some of her challenges and her mom’s support in her interview with Quinn Bradlee:
She counsels parents to be supportive of their dyslexic children – “Stop trying to find a reason why it happened… It’s not your fault… Pay attention to how your child is doing stuff.”
Then, listen to her speak at the Goodwin College 2018 Commencement where she counsels the graduates, after receiving an honorary Doctorate of Humane Letters.
How can you build your child’s self-esteem at home to combat the negative labels in school?
Knowledge…learning…education, fueled by literacy, are keys to success.

Traditionally, literacy is defined as the ability to read and write.
A more complete definition, however, encompasses listening, speaking, reading and writing and today, using electronic media.
The major goal of every educator and parent should be to instill in children a solid foundation of transferable skills and a life-long love of reading and learning. To stay relevant, our children must constantly update their knowledge base. Hence, the prioritizing of literacy.
Dr.Carol Flexer, professor of audiology at the University of Akron, explains the importance of literacy this way,
“Literacy is inextricably entwined with sound. Immature listening abilities and underdeveloped auditory feedback loops have a substantial impact on how children learn to read.”
Literacy is all about sound. All its components incorporate sound in some way. Children learn to speak from listening. They learn to read from speaking and to write from reading.
Although our ears are the conduits for sound, we hear with our brains. Human development studies tell us that the human auditory brain structure does not fully mature until around age 15.
When brains do not receive intact sound, it is usually due to any one or a combination of factors, which include a noisy environment, ear infection, lack of auditory experience or immature brain development. Dyslexics have trouble connecting the sounds that make up words with the letters that represent those sounds. For them, the problem is often immature brain development.
Brain development studies show that sensory stimulation can influence growth and organization of auditory brain pathways.
That is why a number of currently available programs are helping dyslexic children develop their language and literacy skills. They are able to stimulate the auditory centers of the brain with precise sound. Music listening therapy helped my daughter tremendously.
This is good news for the dyslexic community.
Does this mean that every dyslexic person who receives this type of stimulation will learn to read at the same level as his non-dyslexic peers?
No.
Just as there is a continuum in the severity of characteristics in dyslexics, there is variety in their response to various sound development programs.
As technology takes over more and more, the skills that dyslexics find challenging are on the decline, while the thinking skills needed in today’s workplace are an integral component of their strengths.
Does interpretation of sound still matter? Yes.
But let us keep things in perspective. The goal is to learn concepts and generate ideas that will serve humanity and improve society.
There’s eye-reading – print books; ear-reading – audiobooks; and finger reading – braille. Whichever method one uses to accomplish this goal, is what’s best for him.
Which method of reading do you and your children prefer?